Choose a sub-heading:
- Standard
- Genetics of a ridge
- Genetics us a hnedy
- Příbuzenská plemenitba
- Degenerativní myeolopatie
- Dědičná arytmie u ridgebacků (RR IVA)
- Dilatační kardiomyopatie
BREED STANDARD
Basic data
FCI No..: 146
Group 6: honiči, barváři příbuzná a tribe
Section 3: related breeds
Origin: South Africa
Patronage: JAR

General appearance
Stout, strong, muscular and active dog, symmetrical physique, capable of great endurance with sufficient speed. In adulthood they are sturdy and beautiful animals.
Characteristic
Zvláštností plem your ridge, stripe of hair on the back of growing in the opposite direction to the rest of the coat, which is deemed relevant breeding character. Ridge must be distinct, sharply demarcated, symmetrical. It consists of a front rozšířenéčásti, located roughly at the withers, which consists of two chlupovými faith – crowns (crown) and is called boxing. The whole box has to be as nejsouměrnější. But it must not generate more than 1/3 length of the ridge. Ridge tapers evenly towards the tip of the loin and its width does not exceed 5 cm.
Indeální shaped ridge

Undesirable, But even permitted forms of ridge. The front is symmetrical, but not the ideal shape.

Wrong, undesirable ridge shapes. The front part is an elongated (beliefs are not against each other), irregular, too small, or too large, stripe is generally short, too wide or irregular. Ridge with one, or more than two beliefs.

Temperament
Dignified, intelligent, reserved towards strangers, but no signs of aggression or fear.
Head
Moderately long, elongated skull, flat skull, fairly broad between the ears, no wrinkles at rest. Stop: Well defined. The nose is the color of hair black or brown. The muzzle is long, deep and strong, lips are dry and tight.
Eyes
Set moderately far apart, Round, clear and bright with an intelligent expression. Eye color corresponds to coat (učerného nose dark, brown nose by amber).
Ears
Fairly high, medium, rather wide at base, towards the rounded tip gradually tapering. Lying close to the head.
Teeth
The strong jaws, a perfect, regular and complete scissor bite. It stands straight in the jaw and, particularly the canines and well developed blockbusters.

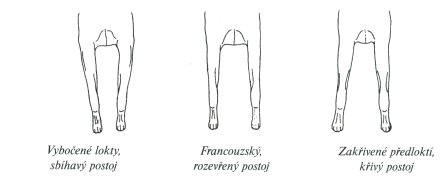
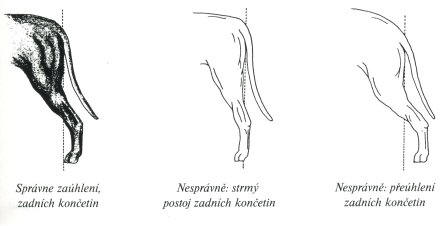
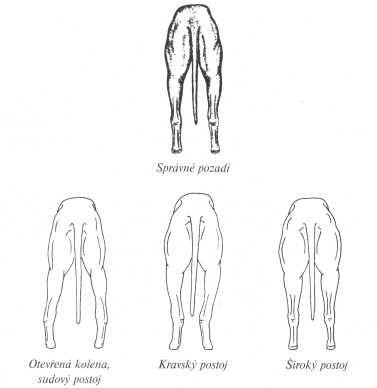
Body
The front legs are completely straight, strong, with strong bones, tight elbows close to body. Shoulders are sloping, lean and muscular. Hind legs are dry, with clearly marked muscle, knee joints are well angulated, hock lies deep.
Tlapy
Compact, with well-arched toes, Round, resistant, pads are elastic, between toes and pads, the hair. 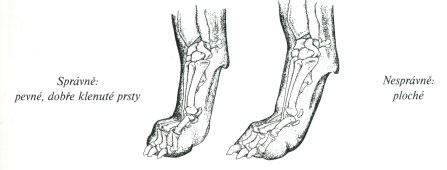
Tail
Strong at the root, is not deployed deep, nor low, towards the tip narrows, is never cumbersome. It is carried slightly upwards, but never curled over back.

Movement
Direct, free and alive.
Coat
Short and dense, smooth and shiny appearance, but never woolly or silky.
Color
Light wheaten to red wheaten. Trunk limbs and tail in a single color. Permits are small white markings on chest and toes, However, many undesirable white markings on belly or above the paws. Nose and ears may be darker.
Size
Withers height: dog 63 – 68,5cm; bad 61 – 66ccm
RIDGE A GENETIKA
Not always the ridge creates an ideal. This is associated with hereditary making such character. Breeding Rhodesian Ridgeback is therefore in the light of a simple ridge. Ridge – inheritance of the Hottentot dogs – was maintained for many, many generations of crossing different breeds of dogs. At first glance, it would therefore appear, already ridge is the dominant character natolik, that can cause a problem in the breed. Ale přece. Parents, who have created the ideal ridge always beget puppies with perfect ridge, but also with unwanted puppies ridge, ba dokonce i štěňata bez ridge. Z toho vyplývá, že ridgeback (s genem = ridge), may be dědičně čistý – „Dominantní homozygot“ = RR or míchaný – „Heterozygot“ = Rr. When the ridge is missing, je pes pravděpodobně „Recesivní homozygot = rr. Tato štěňata without ridge, ale i štěňata s chybným ridge se v chovu zpravidla nepoužívají. Je třeba si však uvědomit, on the contrary,, ne každý pes s ridge na zádech musí být zákonitě ridgeback! Může jít o křížence s jinou rasou. (viz předposlední dvě tabulky – možnosti křížení)
 |
 |
 |
| RR pes s ridge Wear ridgovosti Dominantní homozygot |
Rr pes s ridge Wear bezridgovosti Heterozygot |
rr pes bez ridge Wear bezridgovosti Recesívní homozygot |
The following tables are purely statistical, It is therefore necessary to realize when evaluating litters, that, as regards a tiny litter, některá štěňátka z této statistické pravděpodobnosti se prostě vůbec nemuseli narodit, zanikli a vstřebali se během embryonálního vývoje, which knowledge moves one step back. Only after evaluation of several litters we can assume, jsme objevili already knows SVEMA dogs (feně) RR - vzácného wear ridgovosti. To však ještě stále neznamená, že nemůže mít potomstvo bez ridge. (výzkumy dokazují, že ridge, i když je geneticky založený, nemusí se u každého jedince projevit)
Od roku 2014 se dá vloha pro ridge i geneticky testovat
(více v článku níže)
 |
 |
The ideal combination is, when both parents RR – Wear ridgovosti. The progeny of such an association will continue to give only ridgová puppies. Individuals with RR are beneficial to the holding with respect to the ridge. | |||||||
| RR | RR | RR | RR | RR | RR | RR | RR | RR | RR |
 |
 |
Jeden with rodičů is nositelem Rr (bezridgovosti), However mated RR. From such a connection is born puppies always ridge, but 50% progeny initiatives nositelem gene Rr-bezridgovosti | |||||||
| RR | Rr | RR | RR | RR | RR | Rr | Rr | Rr | Rr |
 |
 |
Both parents do have the ridge, However bearers Rr (bezridgovosti). Here is part of the litter (25%) rodí bez ridge a 50% štěňat is nositelem bezridgovosti. Jena 25% štěňat initiatives nositelem ridgovosti. | |||||||
| Rr | Rr | RR | RR | Rr | Rr | Rr | Rr | rr | rr |
 |
 |
To this combination occurred in Africa, when they were indigenous dogs with ridge wearer RR, crossed with European hunting dogs. All puppies have a ridge, However wearer bezridgovosti. | |||||||
| RR | rr | Rr | Rr | Rr | Rr | Rr | Rr | Rr | Rr |
 |
 |
Tato i předešlá is a combination of bets, to kterému, unfortunately, may today, Ridgeback crosses with another race. Ridge is indeed a major feature of breeding, but beware, Not every dog with a ridge on the back is bound to be ridgeback! | |||||||
| Rr | rr | Rr | Rr | Rr | Rr | rr | rr | rr | rr |
 |
 |
If two bezridgoví individuals mate with each other, can never have ridgové offspring. (even when it comes to purebred ridgeback) | |||||||
| rr | rr | rr | rr | rr | rr | rr | rr | rr | rr |
These tables show the absence of genetics ridge, nepojednávají the formation and regularity ridge. This means, že i když se štěňata narodí s ridge, these may not be the standard ridge. Genetika umístění a tvaru boxu (two crowns), formation and symmetry of the ridge is much more complex and less traceable. Complex genetic pattern is still known. Jen dlouhodobou přísnou selekcí absolutně symetrických a pravidelně utvářených ridge se můžou dostavit chovatelské výsledky. Je nanejvýš pravděpodobné, že původní ridge ani neobsahoval žádný box, ani korunky. Dnešní ridge, jak ho požaduje standard, je výsledkem systematického chovu, čili nově získaným znakem rhodéského ridgebacka.
Rádi byste si otestovali krycího psa a chovnou fenu, jestli bude jejich potomstvo vždy s ridge nebo bude část jejich potomstva bez ridge?
V současnosti je možné geneticky testovat psy a tím rozlišit dominantního homozygota a heterozygota.
Gen pro ridge byl objevený už v roce 2008, avšak genetický test, který by byl k dispozici pro chovatele byl vyvinutý a uvedený na trh až koncem roku 2014 Výzkumným ústavem veterinárního lékařství v Brně www.genocan.eu. Autor testu je Mgr. Miroslav Horňák, Ph.D. Test se vyhodnocuje ze vzorku krve (0,5-1ml odebrané do zkumavky s antikoagulantem EDTA) nebo ze stěru (ústní sliznice speciálním stěrovým kartáčkem).
Stanovením počtu genů pro ridge a tedy genetického založení ridge, může chovatel využít při výběru vhodného partnera při krytí, tak, aby se omezil počet narození bezridgových jedinců. Avšak je dobré vědět, že existuje souvislost mezi počtem „kopií“ pro ridge a výskytem dermoidů. Zvýšení počtu dominantních homozygotů v chovu s sebou může nést zvýšené riziko výskytu dermoid sinus.
Z toho vyplývá, že s informacemi z těchto testů je třeba nakládat v chovu opatrně a rozumně, neměli by být naší prioritou v chovu vrhy se 100% ridgovostí, ani produkování dominantních homozygotů. Conversely, pes bez ridge k chovu našeho plemene patří* a je na zamyšlení, jestli občas takového jedince v chovu nevyužít jako zlepšovatele s ohledem na zdraví v populaci.
*Už od roku 2013 se o tom objevila první zmínka ve zprávě ze zasedání Chovatelské komise FCI konané dne 8. června 2013 v Helsinkách, kde byl přednesený návrh Chovatelské komise schválit do plemenných standardů znaky, kterým je geneticky nemožné se vyhnout, když se chová to, co je plemenným standardem akceptované. V našem případě jde o to, že při chovu ridgebacků není možné chovat to, co standard vyžaduje bez toho, aby se ve vrzích neobjevila štěňata bez ridge, které standard diskvalifikuje (ridgeless).
V některých státech EU hrozí vlády zákazem chovu konkrétního plemene, pokud se standardy neupraví tak, aby tyto „geneticky nevyhnutelné“ modifikace byly stejně akceptované. Prezídium FCI tento návrh postoupilo FCI Vědecké komisi a požádalo Chovatelskou komisi o sestavení úplného seznamu plemen, kterých se tento bod může týkat. V praxi by to pro nás mohlo znamenat legalizace ridgeless v chovu a testy kontrolovaným chovem šanci snížit výskyt DS bez ztráty ridge jako hlavního plemenného znaku.
Autoská práva: Text a kresby: Monika Tušanová, 2003, aktualizované 2014 o nové poznatky v oblasti genetických testů a možnosti testování.
Kopírování kterékoliv části této prezentace jen se souhlasem majitele autorských práv (monika@rr.sk) a překladatele (spsenickova@email.cz)!
Publikováno s laskavým souhlasem autora
Translation: Stanislav Pšeničková
HNĚDÝ NOS
Ridgeback s hnědým nosem?
Year, This option is entirely equivalent to the black nose. It is a matter of taste, who co upřednostňuje, Libi is co mu více. In Slovakia you had seen most ridgebacks with black nose, but more and more popularity and attention gets even livernose individuals. Well pigmented "hnědonosáč" is a real delicacy for connoisseurs ridgebackáře-. Such a dog coat has golden hue and literally in it reflects the sun. The nose is dark brown and brown eye.
Gene for brown nose comes from hunting dogs. Ridgeback it has in its genetic makeup from the time of crossing with pointers. This color is not for Ridgeback Disability. Even the Pharaoh dog comes from the same area as dogs with ridge and livernose, Thus brown gene occurred in the original population of dogs in Africa has always been and still prevalent.
With it týče pigmentace, ridgeback with a brown nose is allowed gene for black.
Must therefore have brown and claws, pads on the legs and contours the eye lids!
View of the well-pigmented hnědonosáče must be as friendly as a dog with a black nose. Unfortunately, the opposite is often true. Since Genetic aspects of black is dominant, born with only a few livernose Ridgebacks. Therefore, breeders trying to breed longed brown nose crosses between them livernose dogs more often than would be appropriate. Occurs causing loss of pigment. Really high quality hnědonosáčů is now very little. Poorly pigmented hnědonosáčovi missing the “life” in the hair, has a liver nose
A světlé, often yellow eye.
Conversely, wise breeders use in their lines brown nose as recovery, because these dogs bring to breed beautiful bright saturated color coat. Breeding only livernose Ridgeback dog leads in both the fading pigment, but also to the loss of hair quality.
Livernose puppies at an early age are azure blue eyes. In adulthood requires a dark amber color eyes, dark brown nose. The color is darker eyes and nose, the better. Adverse are bright yellow eyes and a liver nose. Internationally well-established concept “Livernon” (which means liver nose) is to indicate Ridgeback with brown nose incorrect. Correctly should indicate “brownnose“.
Sample well pigmented dog livernose:

(photo copyright © www.dogworld.co.za)
Jak has to do with genetikou dědičnosti?
B – dominant gene pro černou barvu
b – recesivní gen pro hnědou barvu
This is a very simple type of inheritance. From the genetic point of view is dominant over black and brown. Ridgeback, after their ancestors inherit only one of the three possible combinations of genes. Accordingly, Which one carries in their genetic makeup, Accordingly, in view of the individual gene coloring nose, called homozygous dominant, heterozygous or homozygous recessive.
 |
 |
 |
| BB | Bb | bb |
| dominantní homozygotes Černonosý pes dominant bearer gene for black nose. |
heterozygot Černonosý pes recesivní (hidden) bearer genu pro hnědý nos |
recesivní homozygot Hnědonosý pes does not have the gene for black recesivní nositel genu to brown nose |
USA, or not our Ridgeback bears the gene for brown nose we can confidently say only two:
If our dog livernose (bb) tab 6 or if it has a black nose, but it is a direct descendant of livernose dog (Bb) viz tab. 4,5.
Gene for brown nose, however, may retain the genetic makeup of individuals and several generations of dogs crossing černonosých, where there are often hidden carriers of the gene.
Perhaps a combination of mating
 |
 |
Combination, where both parents černonosí and are also referred to as a gene for black color. The progeny of such an association will continue to give only černonosá puppies, can never be a direct descendant of the brown nose. | |||||||
| BB | BB | BB | BB | BB | BB | BB | BB | BB | BB |
 |
 |
Both parents are černonosí, but one of them is hidden carrier of the gene for brown nose. For such connections are always puppies born with black nose, but 50% offspring will be borne gene for brown nose. | |||||||
| BB | Bb | BB | BB | BB | BB | Bb | Bb | Bb | Bb |
 |
 |
Both parents are černonosí, but both are hidden carriers of the gene for brown nose. Here is part of the litter (75%) born with a black nose (part of which has a gene for brown color) a 25% s hnědým nosem. | |||||||
| Bb | Bb | BB | BB | Bb | Bb | Bb | Bb | bb | bb |
 |
 |
One of the parents has a brown nose, second black. To this combination occurred in Africa, When were the aboriginal dogs with black nose, kříženi s pointery. All puppies have black nose, However a gene for brown nose. | |||||||
| BB | bb | Bb | Bb | Bb | Bb | Bb | Bb | Bb | Bb |
 |
 |
One of the parents has a black nose, the other brown. In this case, however černonosý dog is a carrier of the gene for hidden brown nose, Therefore, the number of pups per litter livernose soaring, 50% litter is livernose, 50% top of the černonosá with genem pro hnědou barvu. | |||||||
| Bb | bb | Bb | Bb | Bb | Bb | bb | bb | bb | bb |
 |
 |
Both parents are livernose. In this case, all puppies in the litter will have a brown nose. | |||||||
| bb | bb | bb | bb | bb | bb | bb | bb | bb | bb |
note:
These tables are purely statistical. It will be appreciated when evaluating litters, that mainly, regarding not numerous litter, Some of the walls of the statistical probability is simply, not necessarily born, disappeared and assimilated during embryonic development.
Source: Taken from the website www.rr.sk Official Website breeds Rhodesian Ridgeback and Thai Slovakia covered SKCHR. Autor: Monika Tušanová
Translation: Stanislav Pšeničková
Note: article did not pass the language revision
Inbreeding AND ITS DETERMINATION
Napsal MVDr. Čestmír Sramek. CSc.
Breeding dogs breeding advisor manages, who is responsible for all breeders level and quality of rearing. Breeding depend on theoretical knowledge and practical experience consultant, its possibilities and willingness to go after shows and dog trials, where has the option itself to assess the results of their work.
Breeding consultant is one person, but among many longtime breeders and experienced breeders, whose knowledge and observations can not be underestimated or even ignored. Therefore I think, that the club members' meeting – discussions in catchment areas are the most appropriate place, where the adviser has to justify their intentions in the farm and carry out evaluation of the results achieved over the past year. The first prerequisite is the personal involvement of breeding consultant on these discussions and further correct questions, comments and suggestions breeders in an open and factual discussion. Only then can move forward in breeding dogs.
Although breeding advisor manages breeding, After all, is not its monopoly position. It must always recommended 3 Dogs, from which the breeder selects one dog at their discretion. There are known cases, the breeder breeding consultant attends in person and stud dog collect together during lengthy discussions of individual breeding dogs. This fact strongly suggests the true interest of farmers on the quality of offspring produced.
Free farming practiced today in some breeds does not always produce the desired results, because breeding work has to do with the whole population of the breed. It is necessary to determine the direction and goal of breeding, which monitors the controlled breeding. A lot of literature and articles in journals devoted to the inheritance and heritability, dealing with theory and practice and correctly indicate the use of progressive methods of breeding.
The aim of breeding work in breeding dogs breeding – ie. continuous improvement of exterior and working properties.
The basic division is as follows breeding:

The breeding dogs are used principally purebred breeding and non-relational and relational. In terms of genetic results we have seen today but not for cross mating of two individuals of the same breed, but various lines (mutually unrelated). Before enrolling males and females for breeding Breeding perform selection – selection. This means, that they come into breeding individuals, who fulfill certain conditions laid down by breeding exterior and evaluation of results on tests. I would like here to point out some facts. Right breed dogs each member club, if the individual has met the conditions set club. Rate but breeding individuals and their contribution to the quality of the population, it is necessary according to the quality of offspring.
The most widespread is the selection in dogs:
- negative – disjunctive, wherein the holding individuals not classified, who do not meet the conditions for breeding. This method is simple, fast, plemenářská but has little effect. Many years to breed not include the individuals with dental defects and these defects are constantly occurring in the population of the breed (podkus, předkus, chudozubost, kryptorchismus, eyelid defects).
- positive – breeding selection means, that the holding classified (selected by mutual mating) two individuals and those with above-average among themselves připařují to improve the quality of offspring.
Per se mating of two individuals above average (Champions) can deliver above-average offspring. In this method, mainly used because of unrelated breeding or very distant inbreeding. Non-relational method in breeding dogs by breeding blue. Nešlechtíme namely quantitative characteristics, which can measure or weigh. Offspring resulting from unrelated breeding is strong, healthy and resilient, but their genotypes and phenotypes. Therefore, even when mating the two above-average individuals mutually unrelated, far below the progeny quality by a parent. Properties such descendants are based heterogygotně and thus the offspring from the same litter appears different level of exterior and work characteristics. Usually you do not find among the siblings in the litter or two individuals, who would have been similar to the other. People can be genetic equilibrium in these offspring called “Each dog – mismatched”.
Relational method of breeding is breeding method progressive, which is used in order to:
- exterior mounting and operating characteristics
- Settling Inheritance
- increase in homozygosity
Prolonged use of inbreeding is reduced viability, Fertility, disease resistance to a weakening of the constitution. For these reasons, it is often condemned by inbreeding breeding method. Opinions zavrhující inbreeding stems from ignorance of its proper use and especially determining the degree of inbreeding. Returning to History, we find, that repeated inbreeding came Thoroughbred (one stallion and four mares) and also the same way bred in England brothers Collingově breed cattle short – horn.
In the implementation of inbreeding is important to perform very strict selection in breeding. Any negative exterior and work characteristics are the cause or disposal of non-breeding. Inbreeding usually ends when reaching the desired properties and the desired rate of homozygosity. Individual, weight Fena, with a higher degree of homozygosity and the required level of exterior and work characteristics, the other is using the ram innovator, meaning, offspring that carries most of its properties. The same method must be preserved even in foreign coverage. It is always desirable to party bitch resulting inbreeding with totally foreign dog (top cross), where the offspring resembles more the mother, than two utterly alien and unrelated breeding incurred by an individual, when the offspring erratic and not far from breeding to meet the conditions, then this coverage yielded nothing for breeding. Hitherto dominated by the older method of evaluating the degree of inbreeding and it is by free generation. Is currently quite imperfect, as it can be properly used only, when the pedigree only found one common ancestor and still the most twice. If a pedigree one common ancestor at least three times or there are two joint and ancestors , has the right to use the coefficient of inbreeding. Its calculation is complicated at first sight, and I do not want to mention more about it. Fx and the index value from zero to one (0-1). Při tom, If less than 0,25 This is a remote inbreeding, when the value of 0,25-0,50 they are inbred and close when the value of greater than 0,50 they are breeding close. Just for fun: když couples Bratři the sestrou, It is available by generations of inbreeding close (no free generation), But when evaluating a coefficient of inbreeding they are inbred remote Fx = 0,12. Prior to the commencement of determining the degree of inbreeding is necessary, seznámit with rodokmenem, in dogs with a pedigree of, but this is also a pedigree.
Pedigree – a list of direct ancestors observed the animal for dogs to fourth generation. Pedigree provides information about the origin of the dog and his pedigree value (estimate the breeding value of an animal by exterior and work characteristics ancestors). Pedigree also used to assess family relationships. Plemenářská practice recognizes 13 species pedigrees.
The breeding of dogs is most commonly used pedigree pedigreed text, common, horizontal.

This family tree is always, father's side of the upper and lower side of the mother's. In determining inbreeding should always seek a common ancestor in the pedigree- ie. one dog or bitch, who are identified in pedigree 2 and one on the side of the father and one mother's side. This common ancestor is marked with one of the listed brands:

If there are two pedigree joint and ancestors, marked each common ancestor with another make.
Determining the degree of inbreeding for broad GENERATIONS
Job generation = Generation, which lies between the generations of parents reporting dog and generations, containing the common ancestor of both the father, tak Matky.
NARROW inbreeding (endogamy / inbreeding) = Is plemenitba, at which the pedigree offspring resulting from inbreeding, occur no free generation. This is a mating father with daughter, matky se synem a bratra se sestrou.

Paris is OTEC x dcera
Among the generations of parents (in which there is a common ancestor and the common ancestor between generations) between 1. ŘP a 2. RP is not no free generation

Paris is bratr x Sestra
Mezieres rodičů generation to generation, containing the common ancestor, (between 1. ŘP a 2. ŘP) shall contain no free generation of both the father, tak Matky.
Nearby inbreeding (intragamie, inbreeding) the plemenitba, at which the pedigree offspring resulting from inbreeding are 1 -2 free generation. It is a mating combinations: grandmother grandson x, grandfather x granddaughter, niece uncle x, teta x synovec, sestřenice x cousin

mate grandfather x granddaughter
Between generations and generations of parents common ancestor (between 1. ŘP a 3. ŘP) is 1 free generation on the mother.

mate uncle x niece
Between parents' generation and the generations to the common ancestor of the father (mezi 1. ŘP a 2. ŘP) does not occur no free generation, but on the mother occurs between generations of parents and the generation of a common ancestor (between 1. ŘP a 3. ŘP) one free generation.

Couples cousin x sestřenice
Between generations of parents and the generation of a common ancestor (between 1. ŘP a 3. ŘP) there is one free generation on the father and one free generation on the mother – or two free generation.
REMOTE inbreeding (intergamie, breeding) the plemenitba, at which the pedigree offspring resulting from inbreeding occurs 3 – 5 free generation.

mate owners and owner
Between parents' generation and generations to a common ancestor (between 1. ŘP a 4. ŘP) There are two free generation of both the father, and on the part of mother – altogether 4 free generation.
If the pedigree is 6 and more free generation, It is a plemenitbu nepříbuzenskou.
DEGENERATIVNÍ MYEOLOPATIE – barebones, VSWR testing in the Czech Republic
Napsal to enjoy Ing. Daniela Čílová
Degenerativní myelopathy (DM) is currently one of the most discussed genetic diseases in Czechoslovakian wolfdog (ČSV). DM was initially considered to be disease specific only for German Shepherds, but was later found to, already jsou postižena i dalí tribe jako velškorgi Pembroke, boxer, rhodéský ridgeback, chesapeake bay retrívr, SAARLOOSWOLFDOG and unfortunately Czechoslovakian Wolfdog.
DM is a progressive neurodegenerative disease of the spinal cord. Early stage disease is manifested by depletion of spinal cord white matter, especially in the thoracic region of the spine. This leads to a gradual distortion of the "paths" leading signals from the brain to the destination and thus to impaired ability to control the rear, and later in the disease, and forelimb. Clinical manifestation in animals affected by the disease is characterized by a style of walking, resulting in loss of balance and co-ordination. Other symptoms include incontinence and progressive paralysis of respiratory muscles. All changes accompanying the degenerative myelopathii are irreversible and worsening in his speech. The first symptoms of the disease are observed approximately at the age of eight and the whole process can take up to three years, in case of, the owner before the animal would not consent to euthanázii. DM is unfortunately currently incurable disease, always ends in death of the animal.
Based on extensive genetic analysis comparing healthy and diseased dogs of several breeds in 2009 American team of scientists managed to identify the probable cause of this disease. This is due to point mutations in the SOD1 gene, referred to as. Each individual has in their cells two copies of this gene and DM are clinically effective only if, that both copies of the gene defective (talking about recessive type of disease). Individuals with one affected (so. mutated) and one "normal" copies of the gene or with both "normal" copies of the development of the disease not. Although DM is strongly determined genetically, Similar to hip dysplasia (£), may play an important role as well as environmental conditions. Among the important factors include the weight of the dog, work or sport activity, housing and general state of health. For this reason, you can not declare with absolute certainty, in animals with damaged both copies of the gene SOD1, the animal will be healthy and that patients, or on the basis of genetic analysis. However, for such individuals, the probability of a disease outbreak is very high.
The test results can be used as useful information in setting up breeding pairs and thus controlled breeding. Whereas, that the manifestations of illness are often at the very end of their productive age of the animal, it is very important to test the dogs name, before they are included in breeding. At present, in CSV selected for HD and ED is monitored (elbow dysplasia), not nearly as serious diseases such as DM. On HD or ED is mostly dying. Testing the DM is not yet mandatory, but in the interest of farmers should be making use of such connection, where at least one of the parents is tested and plain mutated gene. Another defense against the disease exists. According to estimates, and current results in test animals, we can assume, that the population will be approximately CSW 50 – 60 % healthy dogs, 40 % přenašečů a (maybe) 5 – 10 % dogs sick, considered globally. It should be understood, that, like the dog plain mutated gene, tak i pes, carrying one copy of the defective gene (přenašeč) during his life become sick. For this reason, in any way necessary, a ani žádoucí, be excluded from breeding animals - transporter. Breed breeding base is too small for so drastic intervention. Within a few years, we are due to a drastic reduction in the size of the gene pool of the breed to wait more, perhaps even more serious inherited diseases. Reproductions must continue to animals healthy and Carriers.
It should be understood, that DM is not new chrobi, which breed provevuje over the last few years, Do naopak, DM in the breed has always existed, Only we did not have available the appropriate tools, which it demonstrated. Its symptoms are often confused with symptoms of HD.
Department of Genetics and Breeding of the Czech Agricultural University in Prague started research work on the topic Degenerative myeolopatie in Czechoslovakian wolfdog. During the next year we would like to take samples of DNA from the largest possible number of males and females. The exact date of the subscription will be discussed with representatives of the Kennel Club CSW in the Czech Republic and will be published in a timely manner through Newsletters, Club website, případně Wolfdogu. It appears appropriate to a club event, to bring together a significant number of dogs.
Ideal material for DNA isolation is undoubtedly a blood sample. Blood collection at events held in the field, such manifolds, bonitace, meetings and exhibitions, is rather complicated matter. Both in terms of stress to the animals, and in terms of required presence of a veterinarian and related financial website. For this reason, we chose to receive the buccal mucosa. Tako method is ideal for our Terms and trust, so that we will remove disproportionate amount of dogs than it would be within the blood. It is essentially only the gain of the cells from the oral cavity of a dog brush sterile. The identity of the animals will be checked and any reader document certifying the origin of the dog, ie. Pedigree, Europas atd. Subscriptions may not be limited to the CSW population of Bohemia, if interested, it is possible to include a research project and dogs Foreign.
The owners and breeders of Cooperation. The greater the number of animals we can remove, the lower the future risk of a combination of inappropriate parental pairs. We would like to, if our efforts remained only at the theoretical level of research, but it was also stated in animal husbandry practices. Results of testing will not be public or publicly available, will be used for remedial action at stud and will be available only CHK and the owner of the animal.
Appendix explaining the various combinations of variants carrying the SOD1 gene in subsequent generations
In the text (viz. above) shown, the disease is caused by a point mutation in the SOD1 gene outbreaks when it is necessary to be in the organism were two copies of the mutated SOD1 gene. A point mutation is, that there was a confusion of one letter of the genetic code for other. In this case, G ("Normální" copy genu) za A (defective copy of the gene). This letter is therefore used as an abbreviation for the type copies of the gene SOD1. Each individual carries in all their cells, two copies of the gene SOD1 with the exception of sex cells (either sperm or vajíčkek), each having only one copy of the gene. Each individual, after the fusion of gametes, 'll get one copy of the gene from the father and one copy from the mother, Therefore, the likelihood of a particular combination of gene SOD1 depend on the, what gene variants had both parents. Individuals with two "normal" copies of the gene SOD1 ie. G / G only produce sperm or eggs with this gene copy (G), but in an individual who has a 'normal' and one copy of the defective (tj. G/A) to produce sperm or ova, part of which carries a "normal" gene copy (G) East nese pGškozenou kopii genu (A). For completeness, jestAiže se u daného jedince nachází dvě poškozené kopie genu (tj. A/A) such as eggs or sperm wearers use a damaged copy of the gene (A).The genotype of our animals with a gene may occur in the following three combinations:
G/G – (dominantní homozygotes) animal is free of the mutant gene and is healthy
G/A – (heterozygot) animal carries one allele of the gene and one mutated healthy, animal is clinically healthy, but may also mutated variant gene transfer to their offspring
A/A – (recesivní homozygot) animal carries two alleles (Variants) mutated gene, in the course of life is high pravdědopodnost disease
Summary for animal husbandry practices:
Both parents are (G/G), then all puppies are healthy (G/G)G/G
If one parent carrier (G/A) and other health (G/G), then some 50% puppies will be healthy (G/G/Ga 50% the vectors (G/A).G/A
If both parents are carriers (G/A), then some 25% their offspring will be healthy (G/G), 50% will be carriers (G/G/Aa 25% the patients (A/A).
If one of the parents is healthy (G/G) and one of the parents sick (A/A), then all puppies will be carriers (G/A).
Is li-jeden with rodičů is přenašeč (G/A) and one is sick (A/A), then some 50% puppies will be carriers (G/A) a 50G/Ahe patients (A/A).A/A
If both parents are sick (A/A), then all puppies are sick (A/A).A/A
Pes (G/G) is healthy and never there not affect DM. His descendants will never be affected, whether they arise from the merger with spoG/G (G/G), (G/A) or (A/A). Use of individuals (A/A) breeding but not desirable - see. below.
Pes (G/A) the přenašeč a DM u nej také neprojeví. The parent pair but there must be a combination of the two parent carriers (G/A), becG/Ae in that case will be a certain percentage of dogs affected. It is always necessary to rule Dorzho combination carrier x parent or health healthy healthy x.
Pes (A/A) is affected and should not be used for breeding. His descendants always extend at least a number of carriers (Viret to the combination of the G / G), or a percentage of the animals affected – in combination with the other parent (G/A), or animals 100% patients in combination with the parent (A/A).A/A
1) Example of calculation:
father: G/G tj. 100% (= 1) spermií nese "normální" variantu genu
mother: A/G tj. 50% (= ½) carries eggs "normal" variant of the gene a= ½0% (= ½) bears damaged (mutated) variantu Genu
Descendants: 50% G/G (½ * 1) a 50% A/G (½ * 1) tj. half and half completely healthy carriers (but healthy)
2) Example of calculation:
father: A/G tj. 50% (= ½) spermií nese "normální" variantu genu a= ½ (= ½) bears damaged (mutated) variantu Genu
mother: A/G tj. 50% (= ½) carries eggs "normal" variant of the gene a= ½0% (= ½) bears damaged (mutated) variantu Genu
Descendants: 25% G/G (½ * ½), 50% A/G (½ * ½ + ½ * ½) a 25% A/A (½ * ½) tj. quarter completely healthy, half of přenašečů (but healthy) and potentially a quarter of patients
graphic explanation:
| otec/matka | A | G |
| A | AA | AG |
| G | GA | GG |
For the team of the Department of Genetics and Breeding of the Czech Agricultural University in Prague
Ing. Daniela Čílová
DĚDIČNÁ ARYTMIE SRDCE U RIDGEBACKŮ (RR IVA)
Autor: Monika Tušanová, zdroj: RR.sk, Choveteĺstvo a genetika
V USA je přístupná nový specifický test pro plemeno RR odhalující mutaci genu u RR, který způsobuje vrozenou arytmii srdce. Jelikož se tato nemoc podílí na náhlých úmrtích mladých ridgebacků v posledních letech, je předmětem dalšího výzkumu nejen v USA, ale i ve Skandinávii. Předmětem zkoumání je také otázka, nakolik spolu souvisí evropské a americké případy arytmií a náhlých úmrtí mladých psů a zda jde o stejnou genovou mutaci.
Co je to Rhodesian Ridgeback Inherited Arrythmia?
Rhodesian Ridgeback Inherited Arrythmia (RR IVA) je dědičné onemocnění, které má za následek abnormality srdečního elektrického systému vedoucí k možnosti rozvoje poruchy srdečního rytmu. V některých případech tato abnormální srdeční činnost může mít za následek náhlou smrt. Doposud evidované případy poukazují hlavně na období od 6 do 30 měsíců věku psa.
Víc o této problematice se dozvíte v pěkně zpracovaném webináři (v angličtině), který se dopodrobna zaobírá danou tématikou zde.
Jak se dá zjistit predispozice na arytmii?
Genetický test vyvinutý v USA může zjistit, jestli má pes DNA mutaci, která způsobuje tuto chorobu. Jestli pes má tuto mutaci, doporučuje se vyšetření srdce „Holter“, které doposud jako jediné umí spolehlivě tento problém diagnostikovat.
Co znamená Holter?
Holter monitoring je způsob posuzování srdečního rytmu a frekvence. Jedná se o 24hodinový monitoring, elektrokardiogram, který zaznamenává činnost srdce psa po dobu celého, jednoho dne a noci se všemi běžnými aktivitami psa. Tento monitoring jako diagnostická metoda se používá tehdy, když pes vykazuje známky slabosti, závratě, letargie, nadměrně lapá po dechu anebo dokonce kolabuje.
„RR IVA“ a testování
Specifické testování na dědičnou arytmii u plemene Rhodesian Ridgeback, nabízí laboratoř v NC State (USA). Vzorky je možné odebrat v pohodlí domova speciálním kartáčkem – stěrem z ústní dutiny psa.
Objednávka testu (stěrového kartáčku) zde.
Chovatelská strategie
Jedinci, kteří mají diagnostikovanou vrozenou vadu srdce, by se neměli podílet na chovu. Je potřebné a též zodpovědné zvážit výběr chovných jedinců při sestavování chovných párů s ohledem na tuto genetickou mutaci a postupně, plánovaně snižovat výskyt mutací v chovu.
Rhodesian Ridgeback Inherited Arrhythmia (RR IVA) na facebooku.
DILATAČNÍ KARDIOMYOPATIE (DCM)
Dilatační kardiomyopatie (DCM) je vážné srdeční onemocnění postihující především velká plemena psů. U většiny plemen je příčina tohoto onemocnění neznámá, so. idiopatická, u některých plemen včetně kníračů je na vině genetika.
DCM se projevuje zeslabením srdečních stěn při současném zvětšení objemu srdečních dutin, přičemž nejdříve dochází k postižení levé části srdce. V důsledku těchto změn dochází ke zhoršení funkce srdce, srdeční sval má sníženou stažlivost a zmenšuje se srdeční výdej. Orgány jsou špatně prokrvené, tvoří se systémové otoky a otoky plic, projevující se dušností a kašláním. Součástí onemocnění jsou poruchy srdečního rytmu a vazivové jizvy vznikající na myokardu.
Klinické příznaky se začínají objevovat mezi 1. – 3. rokem života. Zpočátku se DCM projevuje sníženou tolerancí zátěže a celkovou slabostí. Mohou se objevovat krátkodobé mdloby a kolapsy. Prognóza onemocnění není příznivá, DCM je častou příčinou invalidity a předčasné smrti psů.
Příčinou vzniku tohoto onemocnění u kníračů je mutace genu RBM20. Konkrétně se jedná o 22bp deleci, která posouvá čtecí rámec při syntéze proteinu RBM20. Dochází k předčasnému zavedení stop kodonu a ke změně vlastností a funkce výsledného proteinu. RBM20 váže RNA a působí jako regulátor sestřihu mRNA u skupiny genů podílejících se na rozvoji srdce. Nefunkční RBM20 produkuje aberantní izoformy TTN, genu pro titin, který je exprimován v kosterním a srdečním svalu, kde podmiňuje pružnost sarkomery.
Mutace vykazuje autozomálně recesivní způsob dědičnosti. This means, že se projeví pouze u jedince, který zdědil mutovanou alelu od obou svých rodičů (recesivní homozygot). Heterozygot je jedinec, který získal mutovanou alelu jen od jednoho ze svých rodičů, nevykazuje žádné příznaky a je klinicky zdravý. Mutovanou alelu však může dále přenášet na své potomstvo.
V USA se při výzkumu této mutace nejprve zaměřili na čistokrevné americké Dobermany, plemeno silně náchylné k vývoji DCM. Nejsou publikována žádná data, která by podporovala asociaci této mutace s nemocí u jiných plemen psů, ale ani u Dobermanů tato mutace není stoprocentně prediktivní, že pes onemocní DCM. Nejen, že má neúplnou penetraci, existují i další mutace, některé známé a jiné neznámé, které modulují účinky této mutace.
Reference:
Molecular genetic studies of canine inherited diseases including SAMS, neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis and dilated cardiomyopathy: Gilliam, Douglas H., Jr., Johnson, Gary S., University of Missouri 2016
V ČR se zatím, tento test provádí pouze u kníračů. Pro Rhodéského ridgebacka není zatím známá kauzální mutace pro vznik tohoto onemocnění.
V SR se v současnosti dají geneticky testovat jenom psi plemene doberman. Test má význam dělat u štěňat, případně dospívajících psů a jeho přesnost se uvádí okolo 70%. U starších jedinců, případně jedinců jiného plemene se doporučuje echokardiologické vyšetření, kterým se DCM dá spolehlivě diagnostikovat. Toto vyšetření se dělá na klinice Sibra v Bratislavě: www.sibra.sk

















